Managing high blood pressure is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing serious complications. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is often called the “silent killer” because it frequently presents no noticeable symptoms until serious health issues arise. In this guide, we’ll explore the symptoms, causes, and effective strategies for managing high blood pressure.
What is High Blood Pressure?
High blood pressure occurs when the force of blood against your artery walls is consistently too high. This can damage your blood vessels and lead to various health problems.
Symptoms
While high blood pressure often doesn’t cause symptoms, some people may experience:
Headaches
Fatigue
Shortness of breath
Dizziness
Heart palpitations
Nosebleeds
Vision problems
Causes of High Blood Pressure
Several factors can contribute to high blood pressure, including:
Age
Family history
Lifestyle factors (diet, exercise, smoking, alcohol consumption)
Medical conditions (diabetes, kidney disease, thyroid problems)
Certain medications
Measuring Blood Pressure
A blood pressure reading consists of two numbers
the systolic pressure (the top number) and the diastolic pressure (the bottom number). A normal blood pressure reading is typically considered to be below 120/80 mmHg. High blood pressure is diagnosed when the systolic pressure is consistently 130 mmHg or higher or the diastolic pressure is consistently 80 mmHg or higher.
The Dangers of Untreated High Blood Pressure
Untreated high blood pressure can lead to serious health complications, including:
Heart attack
Stroke
Heart failure
Kidney disease
Aneurysm
Dementia
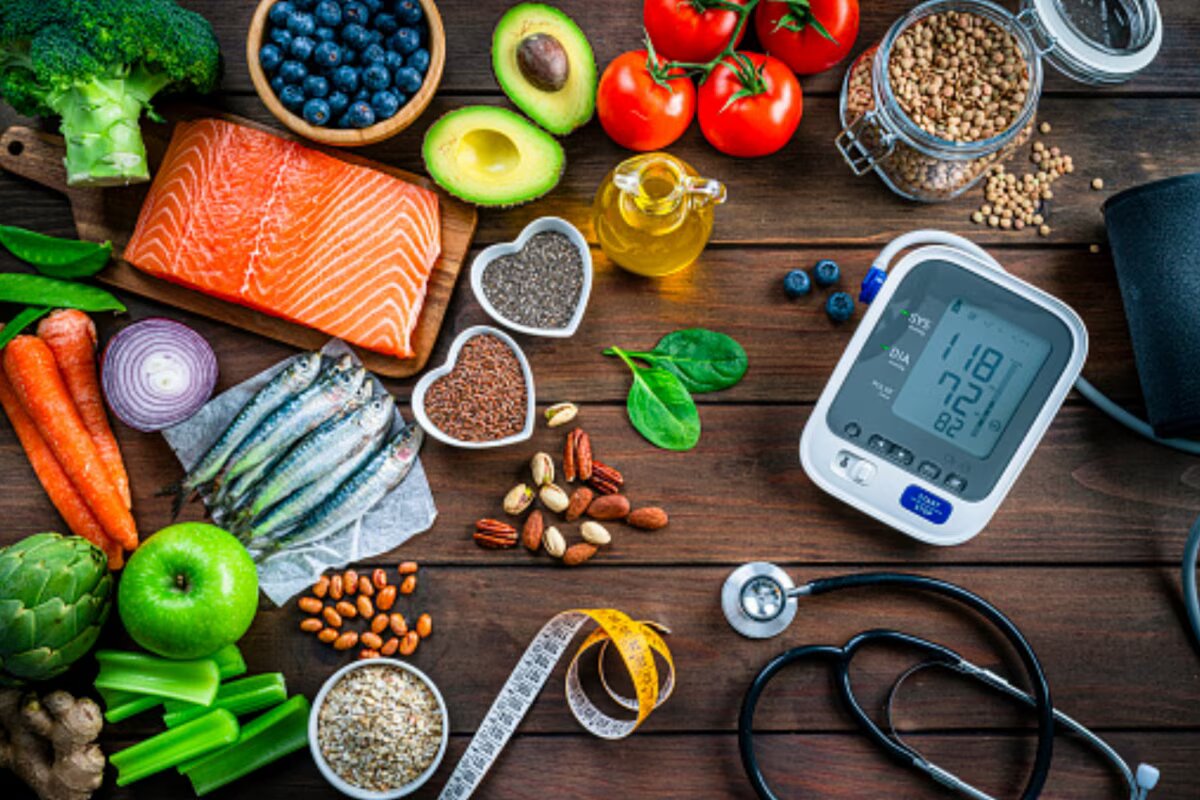
Lifestyle Changes to Manage High Blood Pressure
Making healthy lifestyle changes can help lower and manage high blood pressure. These include:
Healthy diet
Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help reduce blood pressure.
Regular exercise
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Weight management
Losing weight can significantly lower blood pressure.
Limit sodium
Reduce your intake of sodium, which is found in many processed foods.
Limit alcohol
If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
Quit smoking
Smoking can raise blood pressure and increase your risk of heart disease.

Medication for High Blood Pressure
In many cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient to control high blood pressure. Your doctor may prescribe medication to help manage your condition. There are several types of blood pressure medication available, including:
Diuretics
These medications help your body eliminate excess fluid and sodium.
Beta-blockers
Beta-blockers slow down your heart rate and lower blood pressure.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
These medications help relax blood vessels and improve blood flow.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)
ARBs also help relax blood vessels and improve blood flow.
Calcium channel blockers
These medications help relax blood vessels and slow down your heart rate.
Monitoring Your Blood Pressure
Regularly monitoring your blood pressure is essential for managing the condition. You can use a home blood pressure monitor to track your readings and share them with your doctor.
Conclusion
High blood pressure is a serious health condition that can have significant consequences. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options, you can take steps to manage your blood pressure and reduce your risk of complications. If you have concerns about your blood pressure, consult with your healthcare provider. learn more about managing blood pressure through www.webdoctors.com